There are currently some 20 million passenger electric vehicles (EVs) on the road worldwide (according to Bloomberg's annual Electrical Vehicle Outlook 2022 report), as well as 1,3 million commercial EVs (buses, delivery vans, trucks) and more than 280 million electric mopeds, scooters, motorcycles and three-wheelers.
This impressive growth in electromobility, which is expected to accelerate over the next five to ten years, is driven above all by the advancement of battery technology, the commitment of many countries to achieve “net zero” in their carbon emissions and the increase in the production, by car manufacturers, of new EV models that offer users a more reliable driving experience.
Electric Vehicle Power Equipment
In this acceleration of the EV market, the goal is to increase the distances between charges as much as possible. At the same time, there is a need to facilitate accessibility to electric vehicle power equipment, specifically electric vehicle charging stations (ECVE) available to the public.
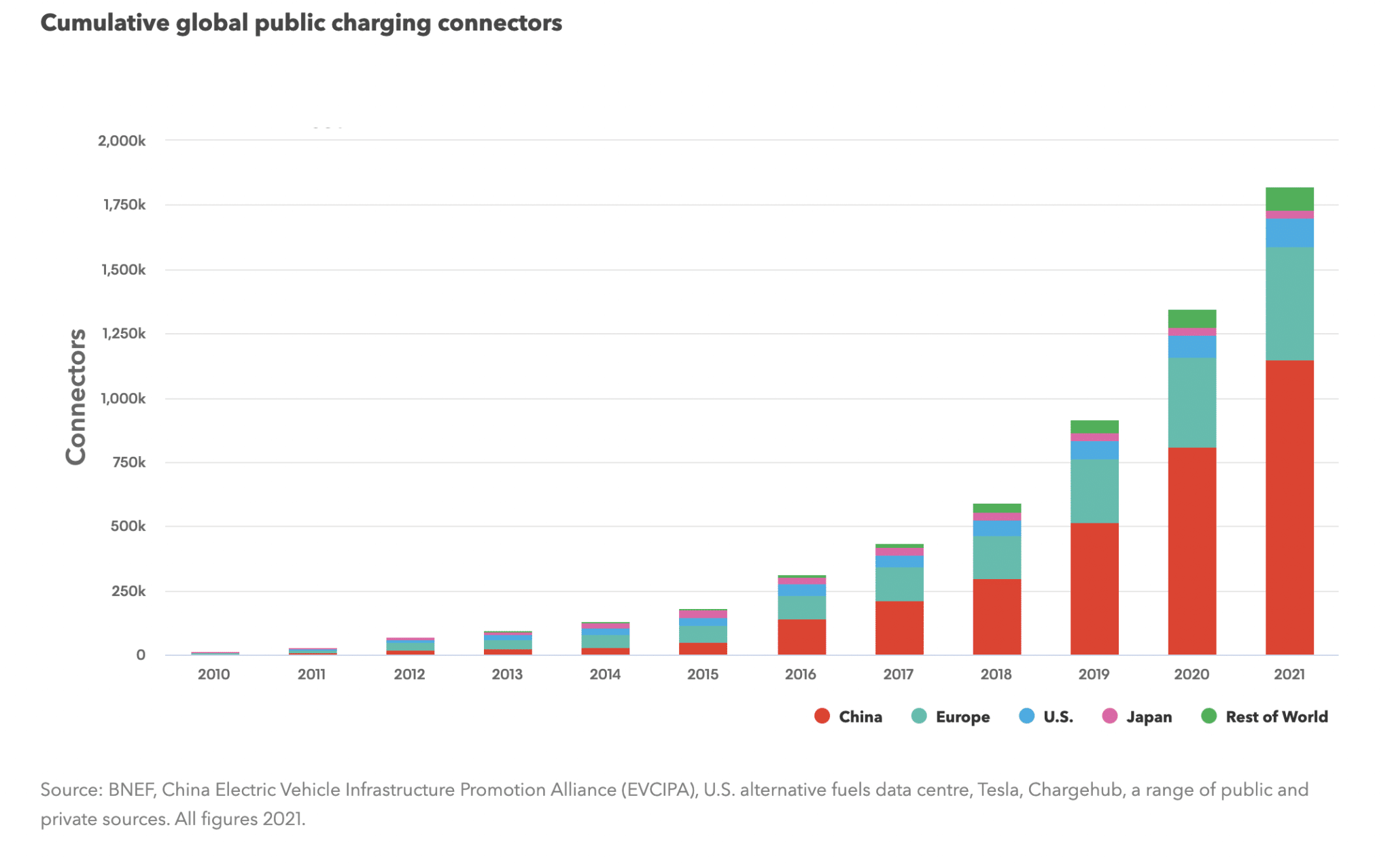
In its 2022 global EV report, the International Energy Agency (IEA) indicates that while most EV charging takes place in homes and workplaces, there were some 1,8 million charging points operating in 2021, of which a third corresponded to fast chargers. Some 500.000 chargers were installed that year, a figure higher than the total number of public chargers available just four years ago. In 2021, according to the IEA, fast-charging ECVEs increased by 48% compared to 43% the previous year, while slow-charger growth fell from 46% in 2020 to 33% a year earlier.
China leads the public ECVEs, accounting for around 85% of the world's fast chargers and 55% of the slow chargers. In Europe there were more than 300.000 slow chargers in 2021 after an annual increase of 30%. By country, there were more than 80.000 slow chargers in the Netherlands, 50.000 in France, 40.000 in Germany, 30.000 in the United Kingdom, 20.000 in Italy and just over 12.000 in Sweden and Norway.
Quick and accurate measurements
To meet the demands of this burgeoning market, electricians and installation engineers need better access to the right tools during commissioning and periodic maintenance. These instruments would include the most advanced models of electrical testers, insulation testers, thermal imaging cameras, and EV power equipment testers. The goal is to enable technicians to take measurements quickly and accurately for efficient testing and troubleshooting. One of the difficulties in particular with Mode 3 AC fast charging stations, which provide accelerated charging from 3,7 kW to 22 kW, is that they supply a single or three-phase voltage with a 230 V or 400 V mains voltage. , so it is essential that they maintain the highest levels of protection when installing, testing and maintaining advanced ECVE.
It is vitally important to ensure reliable communication between the charging station and the EV in order to have an output voltage. To do this, it is necessary to resort to an ECVE adapter that can simulate an EV connected to the charger and check its output voltage with type 1 and 2 connectors in compliance with IEC/HD 60364-7-722 and IEC/EN 61851- 1. Other tests that technicians must carry out are checking conductor continuity, insulation resistance, automatic power disconnection (loop impedance, RCD or RDC-DD test) and functional tests. All of them can be carried out by means of a multifunction installation tester.
Troubleshooting and commissioning
Other instruments required by electricians and installation engineers in order to address the proliferation of ECVE are voltage testers, current clamps or open clamp testers capable of measuring voltage and current without the need for test leads.
Similarly, modern digital insulation resistance testers are ideal for insulation troubleshooting and commissioning, as well as preventative maintenance applications. Also, using a thermal imaging camera in conjunction with a multi-function facility tester or digital multimeter allows technicians to identify any issues within seconds. Portable oscilloscopes that have been designed for motor drive analysis and troubleshooting are especially well-suited for operation in harsh and hazardous environments, as they are instruments that offer the performance of a benchtop oscilloscope, multimeter, and a paperless recorder.
Other useful tools for the ECVE tester are earth resistance clamp meters and battery analyzers, which are designed to test stationary batteries and battery banks. They measure the internal resistance of the battery, AC and DC voltage, AC and DC current, ripple voltage, frequency and temperature.
Who will be in charge of installing and maintaining the infrastructure?
A major problem related to the commissioning and maintenance of these new ECVEs is the worldwide shortage of electricians specialized in this work. For several years there has been a marked decline in the number of experienced installation technicians in the electrical sector, many of them retired after reaching their retirement age, and at the same time most of the new staff have not yet received the level training required.
A particularly marked deficiency in them is a lack of practical training to ensure that test technicians are able to accurately interpret what their advanced test equipment indicates, so that they are in a position to act appropriately.
Some mistakes can be fatal
ECVE testing training is essential for many reasons. One of them is of course the protection of technicians, as well as allowing them to address the growing demand for testing in the EV charging industry and helping them document a complete installation so that they can ensure that it is running smoothly. sure. Electricians who are better trained and more knowledgeable about ECVE commissioning and maintenance can significantly increase their productivity. An inadequately trained installation technician cannot perform a task and therefore increases downtime, as well as making mistakes that could damage expensive equipment. When working with these high-powered equipment, some errors can even be fatal.
Whether it's for regulatory compliance, protection or efficiency, good quality electrical installation training can enhance companies' position for testing and troubleshooting by supporting their employee development goals. Many general electricians are trying to upgrade their skills through certified ECVE testing and installation training plans.
Infrastructure reliability
In general, better-trained staff will help expedite ECVE deployment and thus boost EV uptake. For electrical professionals, ECVE installations create new opportunities and an added revenue stream for those with the knowledge, skills and tools to handle high power EV charging. However, the reliability of EVs and their charging infrastructure are the key factors that affect the growth of this market. The European Commission's European Observatory for Alternative Fuels notes that ECVE infrastructure doubled in Europe between 2020 and 2021, and is likely to have doubled again in 2022. This growth is expected to continue to increase in the coming years as The world is moving inexorably towards a greener future and everyone in the industry must be prepared.
More information about electromobility, technology and solutions for ECVE at https://www.fluke.com/en-gb/products/electrical-testing/emobility.